Every year, countless cats make visits to the vet for issues that could have been prevented with a bit of awareness. One might be surprised to learn that dental disease is the most common issue affecting a staggering 70% of cats over age three. This emphasizes the importance of not just regular check-ups, but also vigilant home care.
Among the top 10 most common diseases, feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) has seen a steady rise over recent years. Historically, improper diet has played a significant role, but enlightened owners are now turning to high-quality, low-magnesium food as a solution. The collective experience and research point towards proactive measures as the best defense against these ailments.
- Dental Disease
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
- Obesity
- Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)
- Heartworm Disease
- Upper Respiratory Infections
- Diabetes
10 Most Common Cat Diseases Every Owner Should Know
Cats are beloved companions, and their health is a top priority for owners. Among the 10 most common cat diseases, dental disease is right at the top. It’s shocking to know that cats as young as three years old can suffer from dental issues. Obesity is another prevalent condition affecting cat health. Overweight cats are more prone to diabetes and joint problems.
Feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) can cause a lot of discomfort for your furry friend. Cats with this disease often have difficulty urinating. Stress and diet play a big role in this condition. Chronic kidney disease is a severe health concern seen mostly in older cats. Regular check-ups can help catch it early and improve outcomes.
Feline leukemia virus (FeLV) is one of the leading viral threats to cats. This virus weakens your cat’s immune system, making them vulnerable to other illnesses. Vaccination is the best way to protect against FeLV. Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) is similar to FeLV, but it progresses slower. Cats can live long, happy lives if managed properly.
Symptoms of common cat diseases include a wide range of signs. These can be weight loss, bad breath, or excessive thirst. If you notice any changes, it’s vital to consult a vet. Preventive measures such as vaccinations and proper diet are essential. Here’s a quick list of common preventive practices:
- Regular vet visits
- Proper diet and exercise
- Routine dental care
- Vaccinations
Dental Diseases in Cats
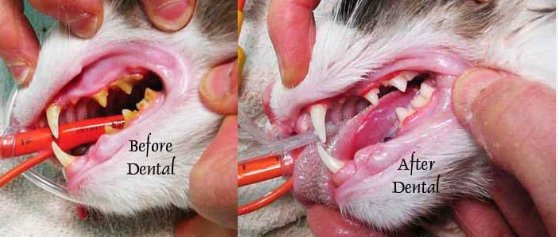
Dental diseases are common in cats, especially as they age. Gingivitis is the most frequent starting point. It occurs when plaque builds up along the gum line. If not addressed, it can progress to periodontitis. This can lead to tooth loss and pain for your cat.
Another common issue is feline tooth resorption. This is when the tooth structure begins to break down and absorbs back into the body. It can be quite painful, making it hard for cats to eat. Regular dental check-ups can help identify this early. Treatment often involves removing the affected tooth.
Signs of dental disease in cats can vary. Some noticeable signs include bad breath, drooling, and loss of appetite. Cats might also have red, swollen gums. Keeping an eye out for these symptoms is crucial. If you notice them, a visit to the vet is essential.
Regular dental care can prevent many of these issues. Here’s a helpful list of preventive dental care practices:
- Regular brushing of your cat’s teeth
- Providing dental treats or toys
- Scheduling annual vet dental cleanings
- Feeding dental-specific diets
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a serious health issue in cats, often affecting older ones. Kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and balancing fluids. When they start to fail, toxins build up in the blood. This can lead to significant health problems. Detecting CKD early can make a difference.
Common symptoms include increased thirst and frequent urination. Cats may also show signs of weight loss and decreased appetite. Sometimes, vomiting and lethargy are noticed. These subtle changes might be easy to miss. Thus, regular vet visits are essential for early diagnosis.
Treating CKD focuses on managing the condition as there’s no cure. This often includes special diets to support kidney health. Fluid therapy might be necessary to keep your cat hydrated. Medications can help control nausea and blood pressure. Monitoring the progression is crucial for effective care.
Prevention includes understanding risk factors and timely interventions. Here are a few key preventive measures to consider:
- Regular health check-ups
- Providing a balanced diet
- Maintaining hydration
- Monitoring weight changes
Hyperthyroidism in Cats

Hyperthyroidism is a common condition affecting middle-aged and older cats. It happens when the thyroid gland overproduces hormones. These hormones regulate the body’s metabolism. When there’s too much, the cat’s body speeds up. This can cause various health issues.
Signs of hyperthyroidism can be subtle at first. Cats might show an increased appetite but still lose weight. They may also become more hyperactive and restless. Some cats might start to drink and urinate more often. It’s important to pay attention to these changes.
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism involves checking hormone levels in the blood. A vet can perform these tests during a routine check-up. Early detection can help manage the condition better. Several treatment options are available. These include medication and sometimes surgery.
Medications can help control hormone production. In some cases, radioactive iodine therapy is used. This treatment targets the overactive thyroid. A special diet might also be recommended. This can help manage the condition and improve your cat’s quality of life.
Prevention can be tricky, but regular vet visits are crucial. Monitoring your cat’s behavior and health can catch problems early. Here are some preventive tips:
- Maintain regular vet check-ups
- Monitor weight and appetite changes
- Feed a balanced diet
- Stay alert for any behavioral changes
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease, or FLUTD, is a common issue in cats. It affects the bladder and urethra, causing discomfort. Cats with FLUTD may strain to urinate. They might also urinate outside the litter box. These symptoms can be distressing for both cats and their owners.
Several factors can contribute to FLUTD. Stress in the home environment is often a big trigger. Diet also plays a vital role in this condition. Cats on dry food diets may be more prone to FLUTD. Increasing water intake can help reduce risk.
Diagnosis of FLUTD involves a physical exam and diagnostic tests. A vet may recommend a urinalysis or X-ray. These tests help determine the underlying cause. In some cases, urinary crystals or stones are present. Addressing the root cause is key to treatment.
Treatment options vary depending on the specific cause of FLUTD. A vet may suggest a change in diet to reduce the formation of urinary crystals. Increasing water consumption is often recommended. In some severe cases, surgery might be necessary. Medications can also help manage pain and inflammation.
Preventive measures are essential to keep FLUTD at bay. Here are some practical tips to consider:
- Provide fresh water daily to encourage drinking
- Feed a balanced diet appropriate for urinary health
- Maintain a stress-free environment
- Ensure regular vet check-ups
Obesity in Cats

Obesity is a growing problem among cats worldwide. It’s not just about a few extra pounds. Being overweight can lead to serious health problems. Diabetes, joint strain, and liver disease are just a few examples. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for a long, happy life.
Several factors contribute to feline obesity. Overfeeding and lack of exercise top the list. Cats who mainly stay indoors are more at risk. They have fewer opportunities to burn calories. It’s important to monitor their food intake and encourage physical activity.
Recognizing the signs of obesity in cats is vital. Your cat may appear less energetic or have trouble grooming itself. You might also notice difficulty jumping or climbing. Weighing your cat regularly can help track changes. Keeping an eye on their waistline is a good practice.
Addressing obesity involves both diet and exercise. A vet can help create a balanced diet plan. Portion control is crucial to avoid overfeeding. Engaging your cat in play can increase their physical activity. Using feather wands or laser pointers can be fun and effective.
Preventive measures can help manage your cat’s weight. Here are some simple strategies:
- Feed measured portions instead of free-feeding
- Choose a diet suitable for their age and activity level
- Encourage regular playtime and interaction
- Monitor their weight and adjust accordingly
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus, commonly known as FIV, is a virus that affects cats globally. It’s similar to the human HIV virus. FIV weakens the cat’s immune system, making them more susceptible to infections. Cats with strong immune systems can live for years after diagnosis. However, keeping them healthy requires some extra care.
The most common way cats contract FIV is through bite wounds from infected cats. Outdoor and male unneutered cats are at higher risk because they often fight. Transmission through casual contact isn’t a concern. Sharing food bowls or grooming each other usually doesn’t spread FIV. Therefore, it’s essential to minimize risks where possible.
Symptoms of FIV may not appear right away. Over time, however, you might notice recurring illnesses or swollen lymph nodes. Weight loss and dental problems are also signs to watch out for. Regular vet visits and blood tests can help catch any changes early on. Early detection allows for better management of the condition.
Currently, there is no cure for FIV, but supportive care can enhance quality of life. This includes a good diet and regular health monitoring. Vaccinations against other diseases remain important too. Reducing stress in their environment can also benefit their well-being dramatically.
Preventive steps are vital even if your cat isn’t infected yet:
- Sterilize your cat to reduce fighting tendencies
- Keep your cat indoors to minimize exposure
- Test new cats before introducing them into your home
- Stay up-to-date with routine vaccinations
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)

Feline Leukemia Virus, or FeLV, is one of the most common infectious diseases in cats. It’s particularly dangerous because it weakens the immune system. This makes cats more vulnerable to other illnesses. FeLV can be a serious threat to cats’ health. However, understanding this virus can help owners better protect their pets.
FeLV is primarily spread through saliva, blood, and sometimes urine or feces. Cats sharing food bowls or grooming each other can inadvertently transmit the virus. Kittens can catch it from their mother during birth or through nursing. Keeping infected and non-infected cats separate is a crucial precaution. This limits the risk of transmission considerably.
Symptoms of FeLV can vary widely. Some common signs include fever, weight loss, and persistent coughing. Anemia and swollen lymph nodes are also potential indicators. Regular veterinary check-ups and blood tests can assist in early detection. Early intervention is the key to better management of the disease.
Currently, there is no cure for FeLV, but treating symptoms can improve quality of life. Regular visits to the vet are essential for managing the condition. Vaccines are available and can lower the chances of contracting the virus. It’s advisable to discuss vaccination options with your vet. This can be especially important for cats that go outdoors.
Prevention strategies can help protect against FeLV:
- Vaccinate cats against FeLV
- Keep cats indoors to reduce exposure
- Avoid bringing unknown cats into your home without testing
- Regularly clean and disinfect shared spaces and items
Heartworm Disease in Cats

Heartworm disease in cats is less common than in dogs but is still a serious health concern. The disease is caused by foot-long worms that live in the heart, lungs, and blood vessels. Mosquito bites generally spread these worms to pets. Since cats are atypical hosts, the worms often don’t reach maturity. However, even immature worms can cause significant damage.
Infected cats may not show signs immediately. When symptoms appear, they can include coughing, vomiting, and lethargy. In severe cases, they might also have trouble breathing. Sometimes heartworms lead to sudden death in cats. Regular vet check-ups can help catch the signs earlier.
Diagnosing heartworm disease in cats can be tricky. Blood tests are typically used to detect the presence of worms. Chest X-rays and ultrasounds might also be needed. There is no approved treatment for heartworms in cats. Instead, vets focus on managing symptoms and preventing further infection.
Preventing heartworm disease is easier than dealing with it after infection. Monthly heartworm prevention medication is effective and easy to administer. Keeping cats indoors can also reduce their exposure to mosquitoes. It’s wise to talk with your vet about the best prevention plan. Taking these steps can protect your cat from heartworms.
Consider these preventive tips:
- Administer monthly heartworm preventatives
- Limit outdoor time, especially during mosquito season
- Install screens to keep mosquitoes out of the home
- Consult your vet for regular heartworm checks
Upper Respiratory Infections in Cats

Upper respiratory infections (URIs) are quite common in cats. These infections are similar to a cold in humans. They often affect the nose, throat, and sinuses. Viruses like feline herpesvirus and calicivirus are frequent culprits. Bacteria can also cause such illnesses in cats.
Symptoms of URIs in cats can vary. They might include sneezing, coughing, and nasal discharge. Watery eyes and fever are also common. Cats may be less active and have a reduced appetite. If you notice these signs, it’s important to seek veterinary care.
Diagnosing a URI typically involves checking the cat’s symptoms. A vet might also perform a physical exam. In some cases, further testing may be needed. Identifying the specific cause of the infection can help direct treatment. Treatments often include rest, hydration, and, if necessary, antibiotics.
Preventing upper respiratory infections involves good hygiene and care. Keeping your cat’s living area clean helps reduce risk. Vaccines can also prevent some viruses responsible for URIs. Regular vet visits are key to maintaining health. Discuss vaccination options with your vet for the best plan.
Consider implementing these preventive measures:
- Ensure regular vaccinations for your cat
- Keep living spaces clean and sanitized
- Limit contact with infected animals
- Provide proper nutrition to boost the immune system
Diabetes in Cats
Diabetes in cats is a condition where there is too much sugar in the bloodstream. It occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose. Without it, sugar builds up, leading to high blood sugar levels. This condition requires careful management.
Common symptoms of diabetes in cats include increased thirst and frequent urination. Cats might also experience weight loss despite eating more. Some cats may act more lethargic or have a dull coat. If you notice these signs, consult your vet. Early diagnosis can help better manage the disease.
Diagnosing diabetes involves blood tests to check sugar levels. A vet may also look for sugar in the cat’s urine. Once diagnosed, treatment often includes daily insulin injections. A prescribed diet helps control blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring is key to managing the condition effectively.
Preventing diabetes can involve maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are some helpful tips:
- Feed a balanced, low-carbohydrate diet
- Ensure regular exercise
- Monitor your cat’s weight
- Schedule regular vet check-ups
Living with a diabetic cat requires some adjustments. You’ll need to follow a consistent feeding and insulin schedule. Also, pay attention to any changes in behavior or health. Support from your vet can make managing diabetes more straightforward. With proper care, diabetic cats can lead happy, normal lives.
Signs and Symptoms of Common Feline Diseases
Cats, like humans, can suffer from various health issues. One common sign of illness in cats is a change in their appetite. They may eat more than usual, or sometimes not at all. Another indicator is unexplained weight loss or gain. Behavioral changes, such as increased aggression or hiding, can also signal health problems.
For respiratory infections, you might notice coughing, sneezing, or runny eyes. These symptoms are similar to a cold in humans. Cats with urinary tract issues often strain to urinate or have accidents outside the litter box. Vomiting or diarrhea can also occur in some cases. Pay close attention to any persistent changes in your cat’s bathroom habits.
Dental diseases are another concern. Signs include bad breath, drooling, and difficulty eating. You might see red or swollen gums. Cats could also paw at their mouth, indicating discomfort. Regular dental check-ups can help catch these issues early.
Changes in energy levels can also be telling. Cats might become lethargic and less playful. On the flip side, they could act restless or overly active. Monitoring these shifts can help pinpoint potential illnesses. If you see any of these signs, seeking veterinary advice is crucial.
For easy reference, here’s a list of common warning signs in cats:
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Coughing or sneezing
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Difficulty eating or chewing
- Behavioral changes
Preventive Measures to Protect Your Cat
Protecting your cat’s health starts with regular vet visits. These check-ups ensure your cat’s vaccinations are up-to-date. They also help catch any health problems early. Routine exams can prevent minor issues from becoming major ones. Always consult your vet if something seems off with your feline friend.
Nutrition plays a crucial role in keeping your cat healthy. A balanced diet supports their immune system and overall well-being. Choose food that suits your cat’s age, weight, and lifestyle. Many low-quality foods are filled with fillers that offer little nutritional value. Always opt for high-quality food recommended by professionals.
Regular grooming is another important preventive measure. Brushing your cat removes loose fur and reduces shedding. This prevents hairballs and keeps their coat shiny. Additionally, it gives you the chance to check for any skin problems or parasites. Cats, especially long-haired breeds, benefit from frequent grooming sessions.
Keeping your cat active is vital for their physical and mental health. Playtime helps burn calories and reduces the risk of obesity. Consider toys that engage their natural hunting instincts. Scratching posts and climbing towers can also provide beneficial exercise. These activities keep your cat entertained and healthy.
Here are some key preventive practices to consider:
- Schedule regular vet check-ups
- Provide a balanced diet
- Ensure regular exercise and play
- Maintain up-to-date vaccinations
The Role of Diet in Feline Health
Diet plays a critical role in maintaining your cat’s health and happiness. A well-balanced diet provides essential nutrients. These nutrients support your cat’s immune system, coat health, and energy levels. Feeding your cat high-quality food is essential. It’s one of the easiest ways to prevent health issues.
Protein is a key component of a cat’s diet. Cats are obligate carnivores, meaning they rely heavily on meat. High-quality protein helps maintain muscle mass. Look for foods with real meat as the first ingredient. Avoid foods with too many grains or fillers.
Hydration is also vital for your cat. Wet food can help ensure your cat gets enough water. This is crucial for urinary tract health. Cats in the wild get most of their moisture from prey. If you feed dry food, make sure fresh water is always available.
Special dietary needs may arise at different life stages. Kitten food typically contains higher protein and fat levels. Senior cats might need foods lower in calories but rich in joint support nutrients. Talk to your vet about the best diet as your cat ages. Monitoring your cat’s diet can help manage weight and prevent disease.
Consider these essential dietary guidelines for your cat:
- Choose high-quality food with real meat
- Ensure balance between wet and dry food
- Provide constant access to fresh water
- Adjust diet according to age and health needs
Importance of Regular Veterinary Checkups
Regular veterinary checkups are essential for keeping your cat healthy. These visits help catch potential health problems early. Vets can spot issues that might not be obvious to you. Early detection can make treatment easier and more effective. By visiting the vet regularly, you can help your cat live a longer, healthier life.
During a check-up, vets examine your cat from head to tail. They check vital signs like weight and temperature. They also inspect the cat’s eyes, ears, mouth, and skin. Blood tests and vaccinations might be part of the visit too. Each of these checks plays a role in ensuring your cat is in good health.
Checkups also provide a great opportunity to discuss any concerns. Whether it’s changes in behavior or diet, the vet can offer advice. You can also talk about preventive measures like flea control or dental care. This helps you keep on top of your cat’s ever-changing needs. Routine visits allow you and the vet to form a comprehensive care plan.
Neglecting regular vet visits can lead to complications. Small health issues can become severe if not addressed early. Routine check-ups can prevent surprising medical emergencies. Here are some key benefits of regular vet visits:
- Early detection of health issues
- Health monitoring and preventive care
- Professional nutritional and behavioral advice
- Update on vaccinations and parasite prevention
Overall, regular veterinary visits are a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership. They ensure your cat is not only surviving but thriving. Making these visits a priority helps maintain the quality of your cat’s life. Investing time in routine care pays off with a happy, healthy pet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cats are susceptible to various diseases that can impact their health significantly. Understanding these common ailments, including symptoms and preventions, can help cat owners provide the best care.
1. What are the signs of dental disease in cats?
Cats with dental disease might show signs like bad breath and drooling. They might also have difficulty eating because of pain or swollen gums. You may notice your cat pawing at its mouth or avoiding hard food.
Regular brushing and dental check-ups play a vital role in prevention. Providing your cat with dental treats and toys can also help maintain oral health.
2. How can I prevent obesity in my cat?
Preventing obesity involves feeding measured portions instead of allowing unlimited access to food. Choose a diet that suits your cat’s age and activity level for optimal nutrition.
Encouraging regular playtime helps keep your cat active and maintain healthy body weight. Monitoring your cat’s weight consistently aids in making necessary dietary adjustments.
3. Why is Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) dangerous?
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) is dangerous because it weakens a cat’s immune system. This makes them more prone to infections and other illnesses despite being slightly infectious through saliva and other bodily fluids.
The virus is often transmitted through shared bowls or grooming each other among cats at home or shelters, as well as from mother to kitten during nursing periods if left untreated without proper vaccination beforehand!
4. What causes upper respiratory infections in cats?
Upper respiratory infections are mostly caused by viruses like herpesvirus or calicivirus. Bacteria sometimes contribute but usually follow viral infection as secondary invaders rather than initial culprits alone due to their role within an existing illness context already present there naturally inherent every day without much notice till triggered off later unexpectedly somehow seemingly against oneself unknowingly altogether inadvertently yet somewhat accidentally occurring likewise nevertheless right alongside anyhow eventually overall unfortunately leading toward undesired consequences ultimately resulting thereafter unexpectedly throughout these events unfolding over time all along slowly then suddenly too soon entirely anyways feeling overwhelmed already now please help someone somewhere here today urgently thank you very kindly indeed ahead sincerely yours warmly forever!
Conclusion
Understanding the various ailments that can affect cats is crucial for their well-being. By being aware of common diseases, owners can take proactive measures. Early detection allows for more effective interventions, improving a cat’s quality of life. This knowledge empowers owners to make informed decisions about their pet’s health.
Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and keen observation are key. These practices not only prevent potential issues but also ensure a happy life for your feline friend. Professional care paired with knowledgeable love provides the best outcome for any pet. This holistic approach forms the foundation of lasting health and happiness for cats.
